01
Sep
Causes, Remedies, and Relief to Stop Tooth Pain

Tooth pain (also called toothache) refers to any pain that a patient experiences in or around their teeth. Sometimes, tooth pain can feel like a sharp pang and, other times, like a dull aching sensation.
Whatever type of tooth pain a person has, it can be quite unpleasant. Toothaches can make it difficult to sleep, trigger a headache, or even limit the types of foods and drinks you’re able to enjoy comfortably. If you have a toothache, you’ll want to find some quick relief.
Tooth Pain Remedies for Fast Relief
Over-the-Counter Pain Medications
Regular pain medications like acetaminophen or ibuprofen can help relieve a toothache.
Desensitizing Toothpaste
Brushing regularly with a toothpaste formulated to desensitize teeth can help combat pain due to sensitivity to temperature changes or sweets.
Topical Ointments
Toothache ointments can provide temporary relief.
Cold Compress
In the event of an infection or injury, a cold compress reduces inflammation and relieves pain.
Clove Oil
Applying clove oil to the affected tooth can help soothe the pain.
Salt Water Rinse
Rinsing with a solution of lukewarm salt water helps control bacteria in the mouth, providing relief.
What Causes Tooth Pain?
Unfortunately, finding relief from tooth pain does not mean that your tooth pain is cured and won’t recur. Quick remedies only help treat the symptoms of tooth pain, but they do nothing to address the underlying cause of your toothache. There are many reasons why people get toothaches including the following:
Tooth Sensitivity
Sensitive teeth are the most common cause of tooth pain. It can occur due to normal wear and tear that erodes tooth enamel, gum disease, bruxism (grinding and/or clenching), and other issues. If you have sensitive teeth, you’ll notice pain when eating or drinking hot or cold foods and beverages or even when biting down on something sugary.
Receding Gums
Sometimes a person’s gums recede or pull away from the teeth. This can happen as a result of gum disease, bruxism, and as a normal part of the aging process.
When the gums recede, the dentin (a porous layer of the teeth) can become exposed. This directly exposes the tooth’s nerves to pressure, temperature changes, and sugar, causing pain.
Broken Tooth
A chipped, cracked, or broken tooth can expose the dentin or even the interior of a tooth where the nerves are located, causing tooth pain.
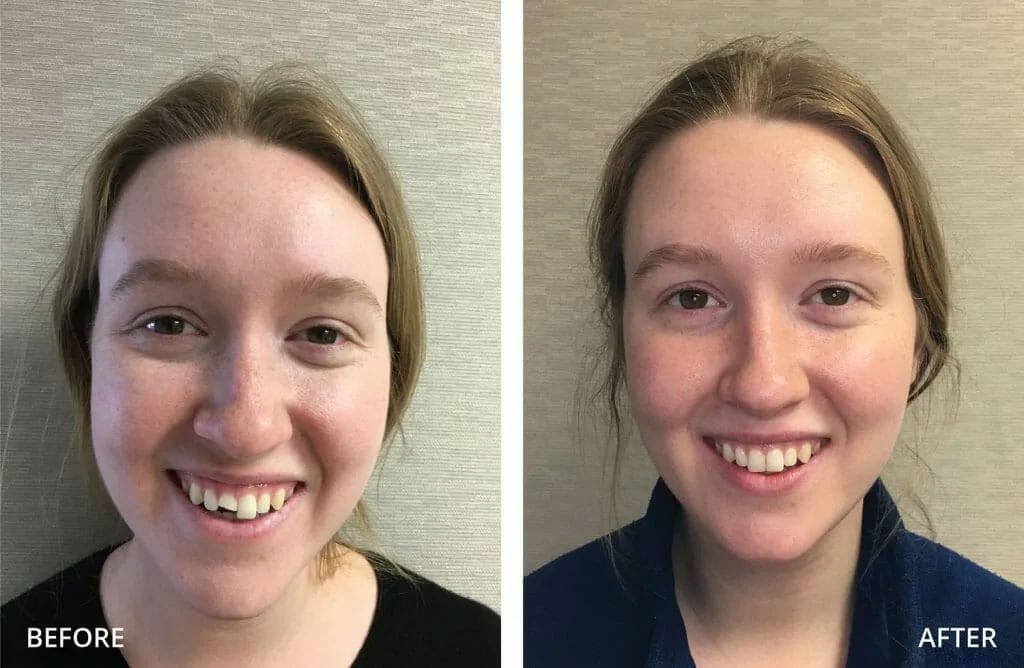
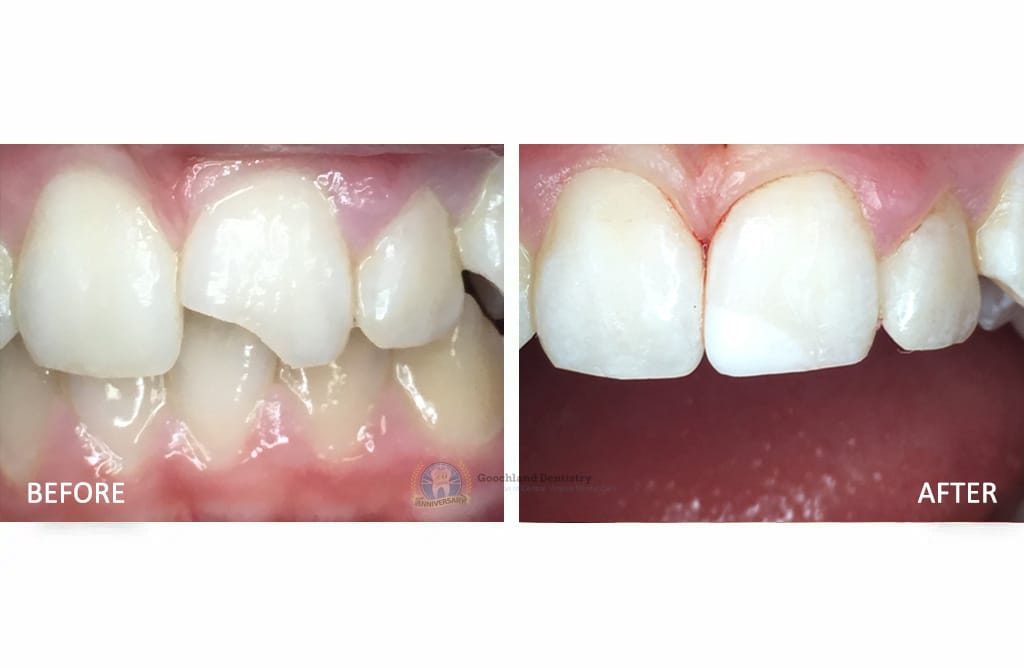
Real Patients Real Results
Before and After Results of Our Patients
- Dr. Murchie rebonded a broken tooth.
- Ms. J had a horse riding accident and broke her front tooth. She wanted to fix her tooth as quick as possible. She had saved the broken fragment of her tooth.
- In about 30 minutes Dr. Murchie rebonded the broken fragment to the tooth and she was very happy.
Tooth Decay
It’s common to experience tooth pain when cavities (dental caries) form in a tooth. Cavities can expose the tooth’s dentin, causing sensitivity. More advanced tooth decay can lead to exposed nerves and/or inflammation and bacterial infections inside the tooth that are also painful.
Infection or Abscess
When the interior (pulp) of a tooth is exposed to bacteria, it can become infected. This can occur as a result of advanced tooth decay, a compromised filling, or when a tooth is broken. Inflammation from the infection causes pain inside and around the tooth.
When the infection spreads, it can create an abscess (pocket of pus near the tooth) that leads to even more localized pressure and pain.
Injury or Trauma
Injuries to the jaw or mouth can also lead to tooth pain.
Wisdom Teeth
Erupting or impacted wisdom teeth can put painful pressure on the neighboring teeth.
Tooth Pain Treatment: When to See a Dentist About Your Tooth Pain
To stop tooth pain at its origin, you’ll need to visit a dentist to determine what’s causing the pain and find an appropriate treatment to resolve the issue.
The treatment that’s right for resolving your tooth pain will depend on the underlying cause:
- Tooth Sensitivity – Sensitive teeth can sometimes be improved with professional fluoride treatments and using toothpaste that contains fluoride. Our dentists might also recommend avoiding foods and drinks that trigger pain.
- Receding Gums – Treatment for receding gums depends on what’s causing them to recede. Our dentists might recommend changing your brushing technique, using a mouth guard at night, and/or professional fluoride treatments.
- Broken Tooth – Depending on the type of damage a chipped, cracked, or broken tooth can sometimes be repaired with dental bonding or a filling. Sometimes, a cap or crown might be needed to support the remaining structure of the natural tooth.
- Tooth Decay – A cavity needs to be drilled, cleaned, and filled to eliminate pain and prevent bacteria from reaching the pulp of a tooth.
- Infection or Abscess – An infected or abscessed tooth can sometimes be treated with a filling. However, when tooth decay has progressed this far, a root canal and cap or crown are usually necessary.
- Injury – Treatments vary depending on the type and extent of injury or trauma suffered. Pain medications are usually recommended to minimize pain until the injury has healed.
- Wisdom Teeth – Depending on whether a patient’s mouth has enough room to accommodate the erupting wisdom teeth, they may or may not need to be extracted.
Schedule a Tooth Pain Appointment at Goochland Dentistry
If you’re experiencing any tooth pain, it’s important to schedule a dental appointment right away. While some causes of tooth pain are fairly harmless (other than the pain), others need to be treated right away to prevent further, more serious health complications. To learn more or to schedule a dental exam with one of our dentists, we encourage you to contact Goochland Dentistry today.